If you have connection issues, flushing your domain name system (DNS) cache might be the solution you need. However, even though a DNS cache can help speed up loading time, it can also cause security issues.
What Is DNS Cache?
DNS cache is a temporary storage of previous DNS lookups in your operating system. When searching for a specific address online, your web browser and operating system will cache the IP address and DNS records. This method streamlines the DNS lookup process by resolving domains to their IP addresses, making web pages load faster for the next visit.
How to Flush DNS Cache
The process to flush your DNS cache will be the same for most Microsoft Windows versions. Keep in mind that you need to use the Run as administrator option when executing the command prompt to access all system security permissions:
Need to open a command prompt. To do this follow the below steps:
1- Hold down the windows key and press R at the same time on the keyboard
2- In the dialogue box type in cmd
3- Then you will get a black windows type in ipconfig /flushdns
4- You should receive the following message
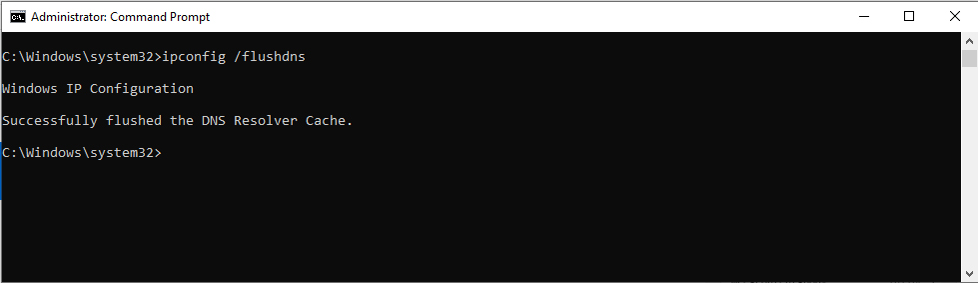
5- Close this window and try your browser again.
Note: You don’t need to worry about a DNS flush having any negative effect on your web experience: after resetting the cache, only the first access of a web project should take a bit longer than usual if it was previously loaded from saved resource records.





